Understanding the Difference Between Dyspraxia and Apraxia
JT
Introduction to Dyspraxia and Apraxia
Understanding the nuances between dyspraxia and apraxia can be crucial for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals. While both conditions affect motor skills, they have distinct characteristics that require different approaches to management and support.

What is Dyspraxia?
Dyspraxia, also known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), is a neurological disorder that affects the planning and execution of physical movements. It can impact a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks, such as writing, dressing, or even speaking clearly. Although dyspraxia does not affect intelligence, it can cause learning difficulties.
Symptoms of dyspraxia may include:
- Poor coordination and balance
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, such as tying shoelaces
- Challenges in organizing thoughts and actions

Understanding Apraxia
Apraxia is a motor speech disorder in which the brain has difficulty coordinating the muscle movements necessary for speech. It is often referred to as Apraxia of Speech (AOS) when it specifically affects verbal communication. Unlike dyspraxia, apraxia is typically associated with damage to the brain, such as from a stroke or traumatic injury.
Common symptoms of apraxia include:
- Inconsistent speech errors
- Difficulty imitating speech sounds
- Groping movements with the mouth while trying to speak

Distinguishing Between Dyspraxia and Apraxia
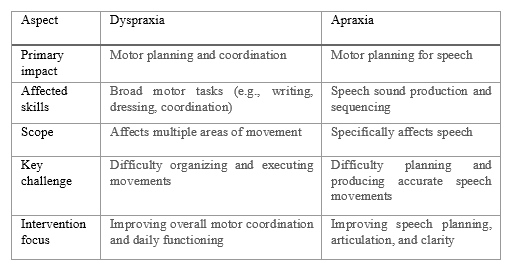
While both conditions involve challenges with motor skills, dyspraxia primarily affects motor planning and coordination across a variety of tasks, whereas apraxia specifically impacts speech production. Understanding these differences is essential for developing effective intervention strategies.
For instance:
- Dyspraxia interventions might focus on occupational therapy to improve motor skills and coordination.
- Apraxia treatment often involves speech therapy aimed at improving articulation and communication.
Below is a comparison table highlighting the key differences:
Approaches to Management and Support
Managing dyspraxia involves a comprehensive approach that may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and accommodations in educational settings. Strategies can be tailored to the individual's specific needs to enhance daily functioning and quality of life.

Apraxia requires specialised speech therapy to develop effective communication skills. Therapists often use repetitive and structured exercises to help the brain form new pathways for speech production.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between dyspraxia and apraxia is key to providing the right support for individuals affected by these conditions. Early diagnosis and targeted interventions can significantly improve outcomes, helping individuals lead more fulfilling lives.
