Reflective Learning: Applying Gibbs' Theory in Education
JT
Understanding Reflective Learning
Reflective learning is an educational process where students critically evaluate their experiences to enhance their understanding and improve future performance. It encourages learners to consider what they have learned, how they have learned it, and how they can apply this knowledge in future situations. This method is particularly effective in developing critical thinking skills and fostering personal growth.
One of the most effective models for reflective learning is Gibbs' Reflective Cycle. Developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988, this model provides a structured approach for reflection, helping learners to systematically analyze their experiences and derive meaningful insights.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
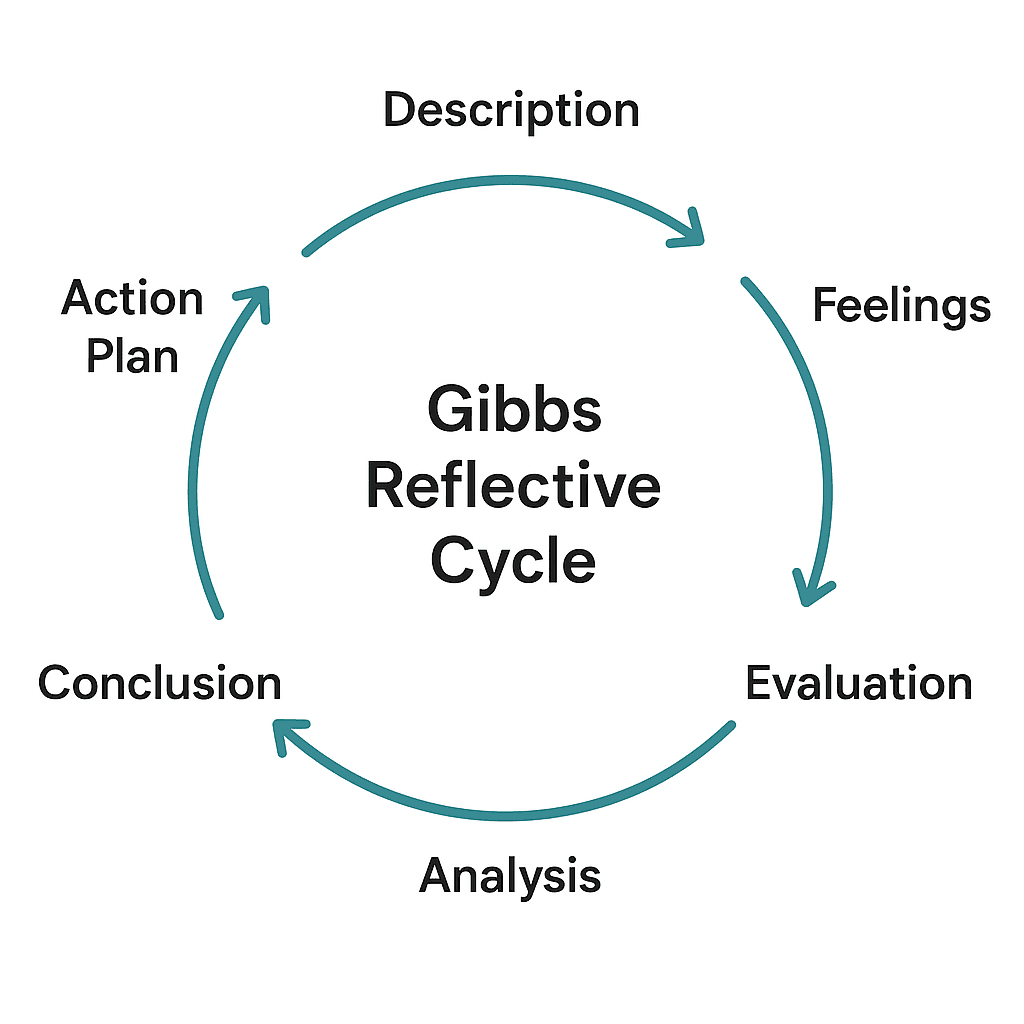
The Cycle is composed of six stages:
- Description
- Feelings
- Evaluation
- Analysis
- Conclusion, and
- Action Plan
Each stage encourages the learner to look at their experiences from different angles, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the situation.
The Description stage involves objectively recounting what happened during the experience. This sets the foundation for deeper reflection without any emotional bias. In the Feelings stage, learners explore their emotions at the time of the event and how these feelings might affect their perception.
Implementing Gibbs' Theory in Education
Incorporating Gibbs' Reflective Cycle in educational settings can significantly enhance learning outcomes. Educators can integrate this model into assignments and classroom discussions, allowing students to engage in reflective practice systematically.
For instance, teachers can assign reflective journals where students document their learning experiences using Gibbs' stages. This not only helps students internalize what they've learned but also allows educators to assess students' progress in developing critical thinking skills.
Benefits for Students
The application of Gibbs' Theory provides several advantages for students. It promotes deeper learning as students are encouraged to reflect beyond surface-level understanding. Additionally, it develops self-awareness, enabling students to recognize and address their strengths and weaknesses.
Through reflective practice, students improve their problem-solving abilities. By analyzing past experiences and planning future actions, they become more adept at handling similar situations effectively.

Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of reflective learning are substantial, educators may face certain challenges when implementing Gibbs' Theory. Some students might initially struggle with articulating their reflections or may find it difficult to express their emotions clearly.
To address this, educators should provide clear guidance and examples of reflective writing. Encouraging an open and supportive classroom environment can also help students feel more comfortable sharing their thoughts and feelings.
Conclusion
Reflective learning, particularly through the use of Gibbs' Reflective Cycle, is a powerful tool in education. It not only enhances academic performance but also prepares students for lifelong learning by fostering critical thinking and self-awareness. By incorporating this approach into educational practices, educators can help students achieve a deeper understanding of their studies and themselves.
Ultimately, the goal is to empower learners to continuously reflect on their experiences, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate future challenges with confidence and insight.
